The Government of India (GoI) had launched India’s first International Financial Service Centre (IFSC) in Gujarat at GIFT City in April 2015. With the launch of the IFSC at GIFT City, the GoI had taken the first step to bring financial services transactions which are relatable to India, back to India. International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) is an initiative by the government of India (GoI) intended to encourage foreign capital to participate in India’s growth journey.
IFSC provides an opportunity to global businesses at GIFT City to set up wide variety of business verticals in Aircraft Leasing, Ship craft leasing, Banking, Insurance, Stock Exchange ,AIF etc by setting company/LLP/Subsidiary in GIFT City.
Table Of Contents
Benefits Of Setting Up A Business Entity At The GIFT City
Infrastructure And Administrative Benefits In GIFT City IFSC
Fiscal Benefits In GIFT City IFSC
Operational Benefits In GIFT City
Conclusion
Why Choose Incorp?
FAQs
Benefits of setting up a business entity at the GIFT City
GIFT City IFSC offers a range of infrastructural, operational, fiscal & tax benefits which make it an attractive destination for businesses and investors, fostering growth and development. The various benefits are listed as under:
A) Infrastructure and Administrative benefits in GIFT City IFSC
1. Ease of doing business: By providing single window clearance, IFSC units can take all necessary approvals under one umbrella (allotment/planning/construction/occupancy) which is useful for IFSC units to set up business in an easy manner.
2. Duty relaxation: Exemption from stamp duty and registration charges provided by IFSC for setting up business entity at GIFT City.
3. Incentives: Development incentives offered by Gujarat Government like Capital Subsidy, employment generation incentives etc to encourage the business setup in GIFT City.
4. Setting up: Plug & play infrastructure, facilitating quick and hassle-free business setup.
5. Cost efficiency: Sustainable development model with a potential 20% reduction in operating costs.
6. Gujarat IT/ITeS Policy incentives: EPF reimbursement, lease rental subsidy, power subsidy, etc.
Related Read: A Complete Overview Of IFSC Gift City And Tax Benefits
B) Fiscal Benefits in GIFT City IFSC
1. Income tax benefits:
For Units in IFSC:
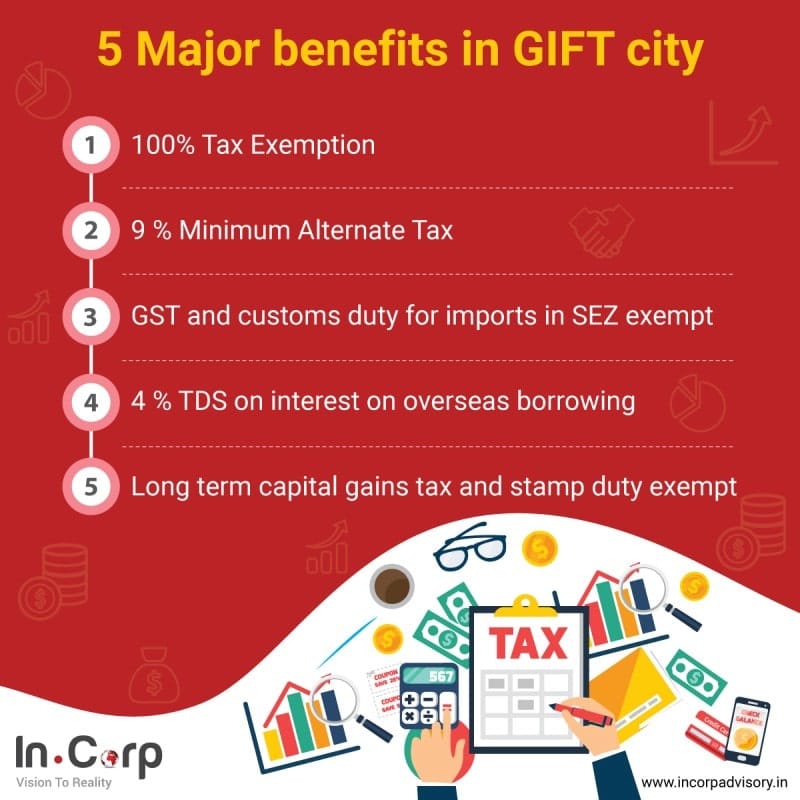
- 100% tax exemption for 10 years out of a 15-year block period
- IFSC Unit has the flexibility to select any 10 years out of 15 years block
- Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT) or Alternate Minimum Tax (AMT) at 9% of book profits applies to IFSC Companies /other setup as a unit in IFSC (Not applicable to IFSC companies in GIFT city opting for new tax regime)
- Dividend paid to shareholders of company in IFSC: From 01 April 2020, dividend income distributed by Companies in IFSC to be taxed in the hands of the shareholder.
For Investors:
- Interest income paid to non-residents on money lent to IFSC units in GIFT city is not taxable, and long Term or rupee-denominated bonds listed on IFSC exchanges are taxable at a lower rate of 4%.
- Transfer of specified securities listed on IFSC exchanges by non-residents is not treated as a transfer, and gains arising from such transfers are not taxable in India.
Related Read: Why GIFT City Is The Better Destination For Stockbrokers
2. Goods and Services Tax (GST) benefits:
For Units in IFSC:
- No GST on services: (i) received by unit in IFSC. (ii) provided to IFSC / SEZ units, Offshore clients.
- GST applicable on services provided to Domestic Tariff Area
For Investors:
- No GST on transactions carried out in IFSC exchanges
3. Other taxes and duties:
For Units in IFSC:
- State subsidies are available for IFSC units like lease rentals, provident fund contributions, and electricity charges.
For Investors:
- Exemption from Security Transaction Tax (STT), Commodity Transaction Tax (CTT), and stamp duty for transactions carried on IFSC exchanges.
C) Operational Benefits in GIFT City
1. Exemption from currency control regulations for IFSC units:
- Units in the IFSC are treated as non-residents, enjoying the benefits of a non-resident under exchange control provisions.
2. Liberalized currency control regime for Indian residents:
- Foreign Exchange Management (Transfer or Issue of any Foreign Security) Regulations, 2004 (“ODI Regulations”) restrict investment by an Indian resident into an overseas firm in the financial services sector.
- To enable, Indian residents to set-up and invest funds in GIFT City, RBI, vide its Circular dated May 12, 2021, has permitted sponsor contribution from a sponsor Indian party in an Alternative Investment Fund (AIF) established overseas, including IFSC.
Related Read: How To Incorporate AIF In GIFT City- IFSC?
Conclusion
Setting up a business entity at GIFT City and capitalizing on these benefits, businesses and investors can harness the immense potential and growth opportunities available at IFSC, GIFT City. Benefits from fiscal, operational, tax make GIFT City an attractive destination for setting businesses. By leveraging these benefits, businesses can unlock growth opportunities and thrive in the dynamic ecosystem of GIFT City.
Why Choose Incorp?
At In. Corp, our team will help you with setting up IFSC units in GIFT and other services at GIFT City:
Setting up IFSC entities at GIFT City, Gujarat: Incorp can help to setup IFSC units at GIFT City within the regulatory framework. These includes selection of appropriate structure, incorporation of the entity, services from identification of office space to incorporation of units and advice on different services offered by IFSCA Authority.
Obtaining SEZ & IFSCA approvals: Incorp will liaison with SEZ & IFSCA Authority for applying, preparing documentation required, obtaining necessary licenses to operate from GIFT City as IFSC unit.
Other regulatory compliances: Incorp will assist you to obtain various initial registrations under Income Tax Act, GST Law, IEC, RCMC etc. and can provide assistance in the various regulatory compliance.